Biopolyethylene, Bio-based Polyethylene,
Green Polyethylene (GPE)
From fossil fuel-based to Bio-based: with a negative carbon footprint from cradle to gate, this biopolymer mitigates the impacts of global warming
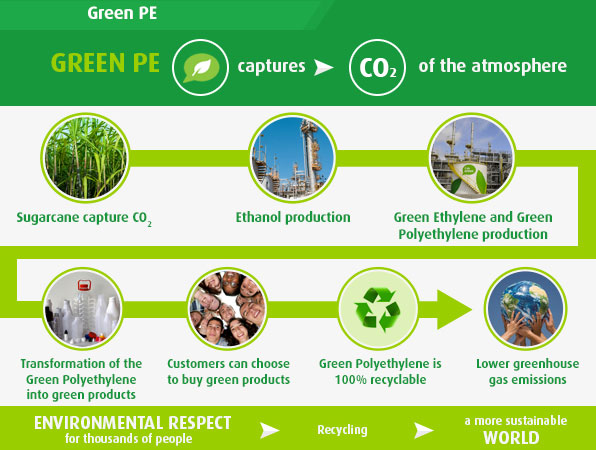
What differentiates this product made from sugarcane from fossil-based products is the use of renewable feedstock, which is derived from the biogenic carbon found in the green polyethylene that is captured during the sugarcane development phase.
Benefit 1: Cutback on greenhouse gas.
Fossil fuel-based PE CO2 emission is 4.57kg CO2/kg PE, but Bio-based polyethylene only emits 1.35kg CO2/kg of PE 70% OFF ! reduction of CO2 emission per kg.
The negative footprint also reflects the reality of Brazil’s sugarcane and ethanol industry. Sugar cane is already recognized as a stable and sustainable resource of bio-ethanol. Commonly planted on degraded pasture land, sugarcane helps recover the soil and consequently increase its carbon content. Moreover, sugarcane bagasse, a waste product from the crushing process, is often used to generate electric power to supply the entire ethanol production process, which makes it energy self-sufficient, while any surplus power is sent to the grid, adding clean energy to Brazil’s energy matrix. Using ethylene made from sugarcane-based bio-ethanol as raw material, Biopolyethylene is produced by the same polymerization process than the conventional procedure. But here, the usage of exhaustible resources and CO2 emissions are drastically reduced.
It’s important to note also that 90% of sugarcane cultivation and harvesting in Brazil is concentrated in the country’s Center-South region, which is located more than 1,200 miles from the Amazon Region.
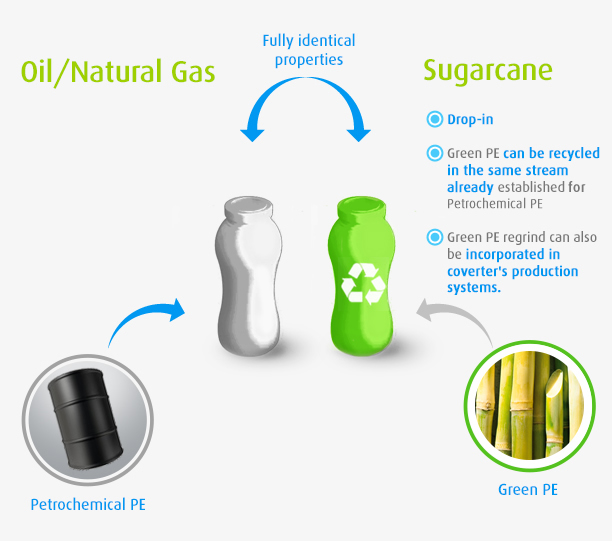
Benefit 2: Same properties/processability as usual PE
Though the starting material is different, they are the same composition as fossil-based plastic, and can be processed and recycled along and exactly the same way as fossil-fuel based LDPE, HDPE and LLDPE.